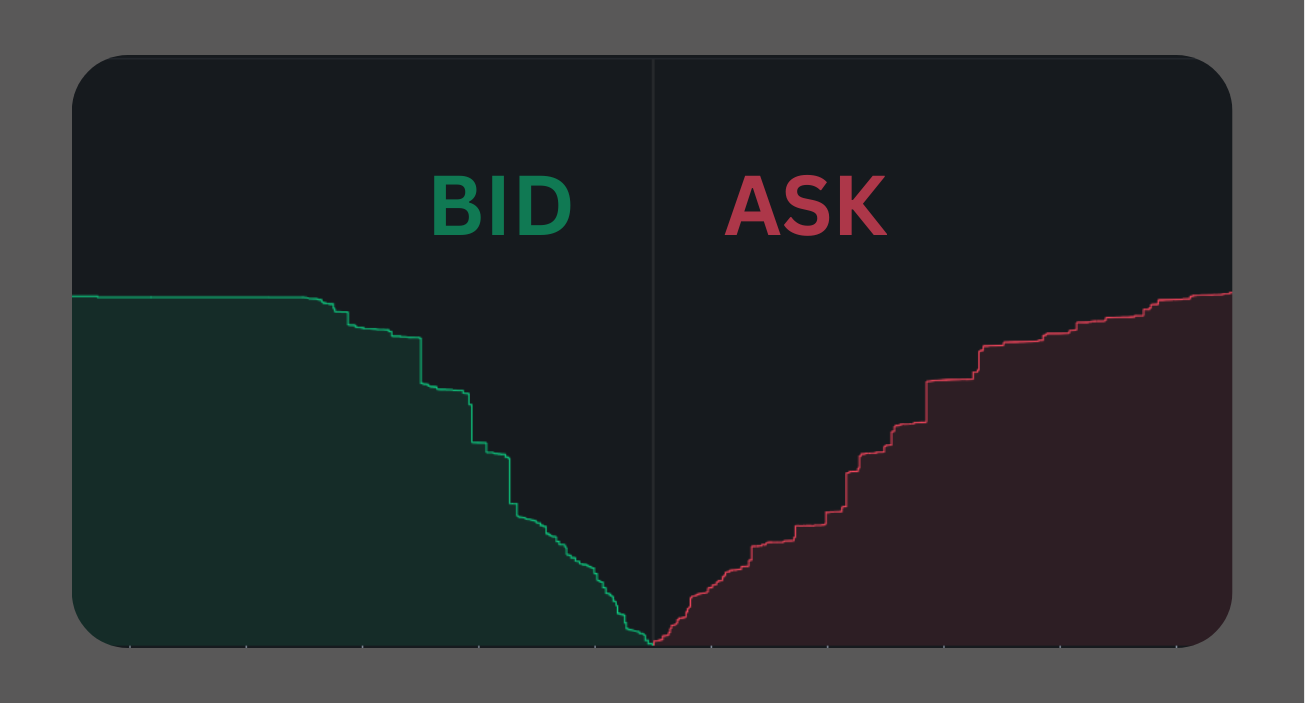
When setting up a crypto exchange, liquidity is one of the most crucial factors for success. Without sufficient liquidity, traders experience slippage, wider spreads, and overall poor user experience, which can drive them to competitors. In this article, we will guide you through the essentials of setting up liquidity on a crypto exchange, covering A-book and B-book models, ECN providers, and rebates for market makers.
Understanding A-Book and B-Book Liquidity Models
Crypto exchanges have two primary methods for managing order flow—the A-book and B-book models. Understanding the difference between these two approaches is essential to decide the best strategy for your exchange.
A-Book Model: In the A-book model, an exchange passes customer orders directly to external liquidity providers or counterparties, usually, it’s the biggest crypto exchanges like Binance, Kraken or OKX. Essentially, the exchange acts as an intermediary, meaning that when users trade, their orders are matched with real market participants outside of the exchange. This model tends to offer greater transparency since the exchange is not directly taking a position against its users. Meanwhile, it requires additional capital provided by the exchange to settle orders on behalf of users.
B-Book Model: The B-book model, on the other hand, involves the exchange taking the opposite side of a user's trade, effectively acting as a counterparty. Here, customer orders are managed internally without being passed on to external liquidity providers. The benefit of this model is the potential for higher profit margins for the exchange, as it captures the spreads. However, this approach requires experience in trading and risk-management since exchanges using this model must manage risks effectively to avoid significant exposure and losing money.
Many exchanges opt for a hybrid approach, leveraging both A-book and B-book models depending on market conditions and the trader's profile.
A-Book Model: In the A-book model, an exchange passes customer orders directly to external liquidity providers or counterparties, usually, it’s the biggest crypto exchanges like Binance, Kraken or OKX. Essentially, the exchange acts as an intermediary, meaning that when users trade, their orders are matched with real market participants outside of the exchange. This model tends to offer greater transparency since the exchange is not directly taking a position against its users. Meanwhile, it requires additional capital provided by the exchange to settle orders on behalf of users.
B-Book Model: The B-book model, on the other hand, involves the exchange taking the opposite side of a user's trade, effectively acting as a counterparty. Here, customer orders are managed internally without being passed on to external liquidity providers. The benefit of this model is the potential for higher profit margins for the exchange, as it captures the spreads. However, this approach requires experience in trading and risk-management since exchanges using this model must manage risks effectively to avoid significant exposure and losing money.
Many exchanges opt for a hybrid approach, leveraging both A-book and B-book models depending on market conditions and the trader's profile.
Leveraging ECN Providers for Deeper Liquidity
Electronic Communication Network (ECN) providers like Finery Markets play a significant role in establishing and enhancing liquidity on crypto exchanges. ECNs function as a bridge between multiple liquidity providers, enabling an exchange to access a broader pool of buyers and sellers. By integrating with an ECN, an exchange can benefit from deeper liquidity, tighter spreads, and faster execution times.With ECN, an exchange can efficiently access liquidity from multiple providers through a single integration, outperforming the standard A-Book model. However, liquidity may be insufficient for assets not on the tier-1 list like trending memecoins.
Rebates for Market Makers: Incentivizing Liquidity
One effective strategy for boosting liquidity is to offer rebates to market makers. Market makers play a key role in maintaining tight spreads and ensuring that traders can execute orders efficiently. By providing financial incentives, such as rebates, exchanges can encourage market makers to place buy and sell orders on the platform.
The rebate structure typically works by rewarding market makers for adding liquidity (maker-side orders). These rebates are often a percentage of the trading fee, which incentivizes market makers to maintain active participation and helps keep the order book liquid.
The rebate structure typically works by rewarding market makers for adding liquidity (maker-side orders). These rebates are often a percentage of the trading fee, which incentivizes market makers to maintain active participation and helps keep the order book liquid.
Balancing Liquidity Strategies for Success
Ultimately, setting up liquidity for a crypto exchange involves striking the right balance between various models and strategies. Here are a few key takeaways:
By effectively managing liquidity, you can create a more efficient trading environment, enhance user satisfaction, and position your exchange as a competitive player in the crypto market.
Advix offers exchanges and wallets a service to boost their liquidity by setting up efficient infrastructure and integrations, intros to market makers with the best offerings, and consulting on liquidity and treasury management.
- A-Book vs. B-Book: Consider using a hybrid model to combine the benefits of both A-book transparency and B-book profitability.
- ECN Providers: Integrate with ECN providers to access a deeper liquidity pool and improve efficiency of integrations.
- Market Maker Rebates: Incentivize market makers through a well-designed rebate program to keep your order book active and attract traders.
By effectively managing liquidity, you can create a more efficient trading environment, enhance user satisfaction, and position your exchange as a competitive player in the crypto market.
Advix offers exchanges and wallets a service to boost their liquidity by setting up efficient infrastructure and integrations, intros to market makers with the best offerings, and consulting on liquidity and treasury management.